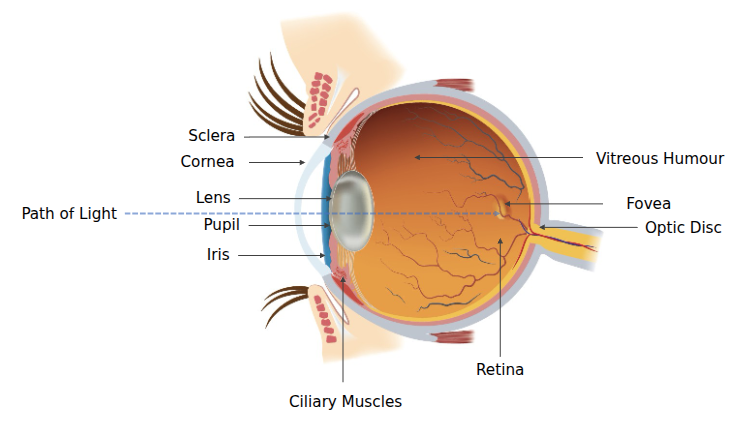
Detailed View of the Retina
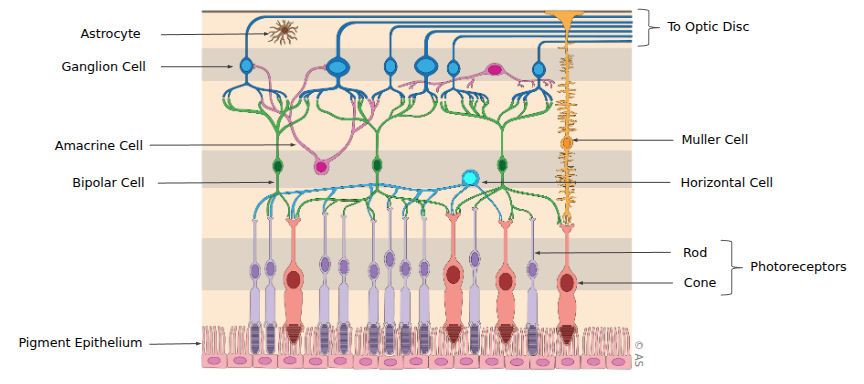
Roles of the cells in the retina:
- Optic Disc where all the information get transferred to
- Astrocyte support cells
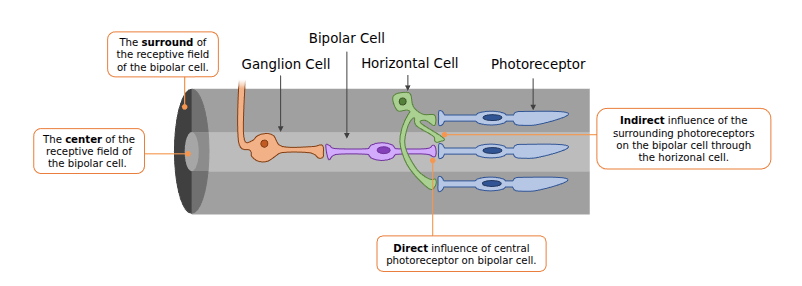
- Ganglion Cell output neurons to the optic disc
- There are three types of ganglion cells
- Parasol
- Midget
- Bistratified
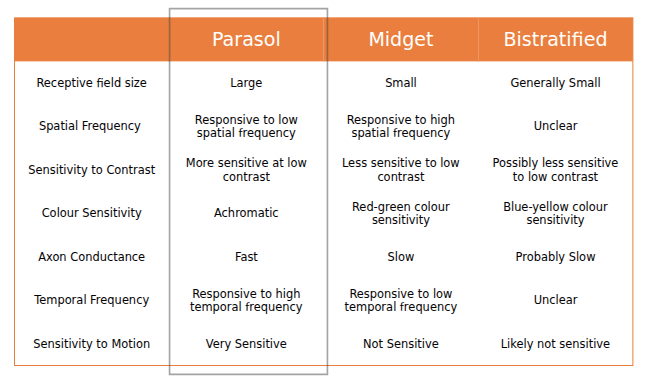
- There are three types of ganglion cells
- Amacrine Cell interneurons for processing
- Bipolar Cell relay neurons
- Horizontal Cell lateral connection neurons
- Muller Cell support cells
- Photoreceptors detect light and connect to neurons
- Pigment Epithelium supports the photoreceptors
Receptive Field
This refers to the field of which a specific cell is responsible for (bigger field means more information). They ganglion cell “sees” a larger area of visual space than a single photoreceptor.
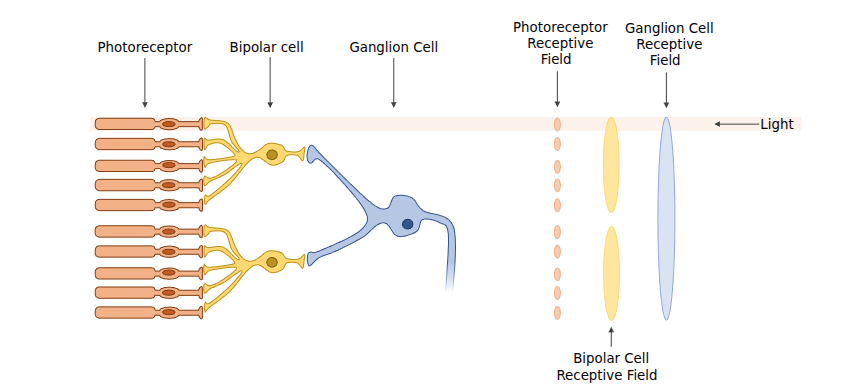
Center Surround Receptive Field
In this setup,
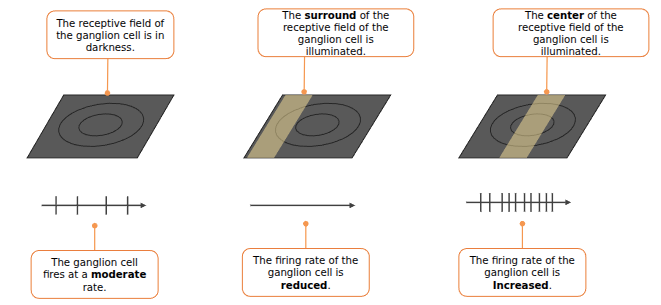
 Researchers found that ganglion cells fire:
Researchers found that ganglion cells fire:
- at a moderate rate when no light exists
- at a reduced rate when light is hitting the surround of the receptive field
- at a increased rate when light is hitting the center of the receptive field
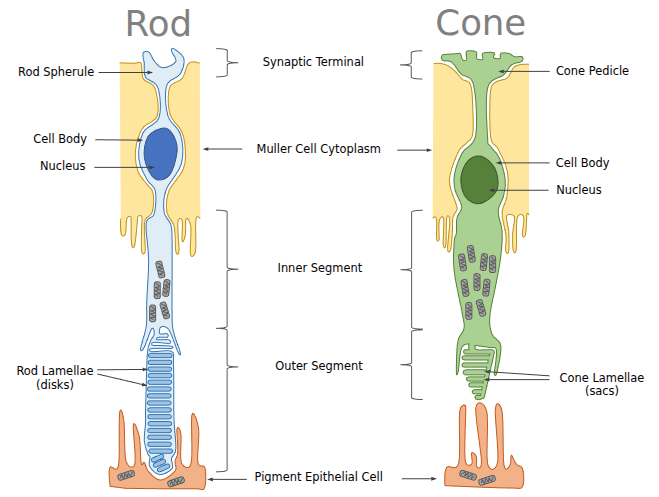
Rods and Cones
Rods are specialized for dim light / night vision.
Cones are specialized for day light and colour
Density of Rods and Cones
As we get near the foveal (center) region of the eye, there are significantly more cones can rods.
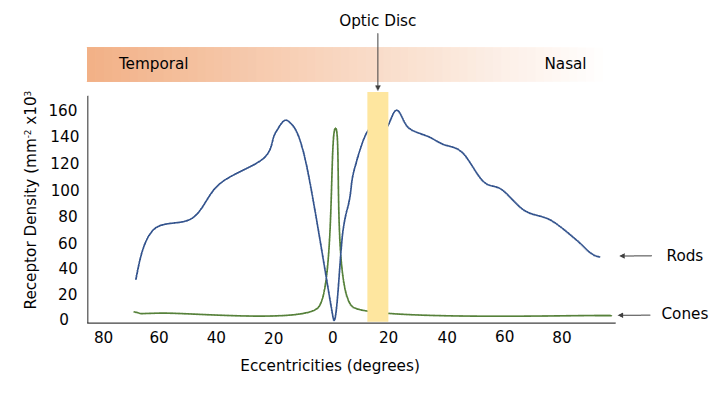 Temporal is the outer edge of your face, nasal is your nose. This is your left eye.
Temporal is the outer edge of your face, nasal is your nose. This is your left eye.
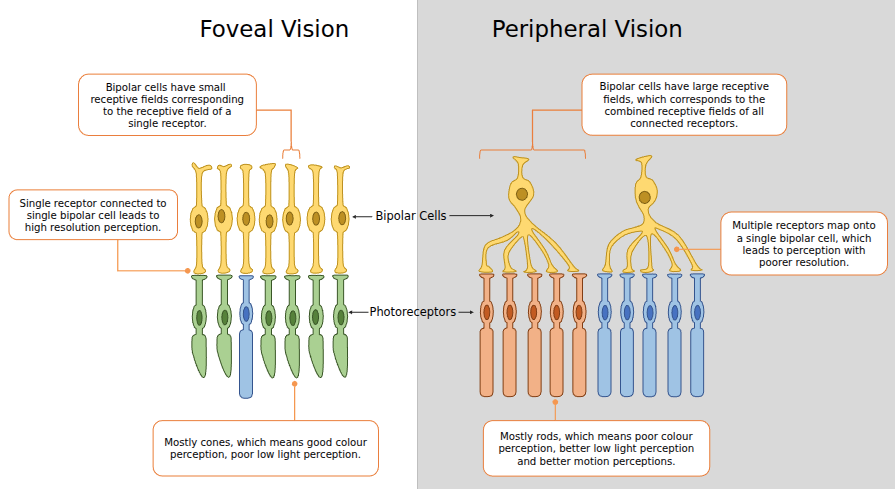
Your peripheral vision has more rods than cones, and the bipolar cells have a larger receptive field. Thats why you have poorer resolution perception near the edges of your eyes.
Direction of Light
Weirdly enough, light travels THROUGH the nerved and into the cones
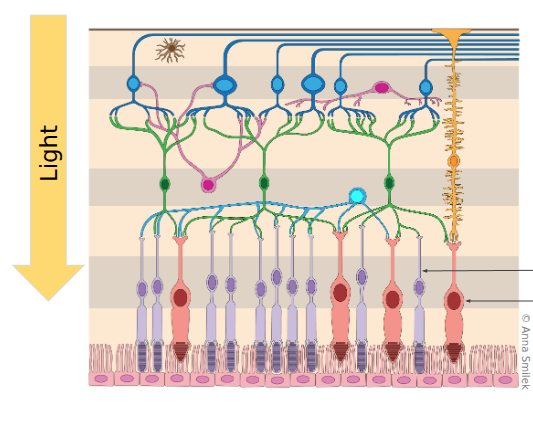 Near the forvea, the nerve cells split apart to make sure as much light touches the cones and rods in the middle as possible.
Near the forvea, the nerve cells split apart to make sure as much light touches the cones and rods in the middle as possible.
Muller cells
Span the entire thickness of the retina and help guide light into the cones and rods. They also provide metabolic support to the neurons.
