Language and the Brain
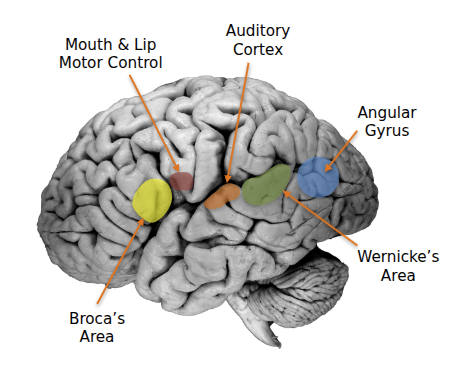
- Brain regions for language:
- Broca’s Area – speech production (in frontal lobe).
- Wernicke’s Area – language comprehension (in temporal lobe).
- Angular Gyrus – reading/writing integration.
- Auditory Cortex – hearing words (primary auditory in temporal lobe).
- Motor Cortex – controlling lips, mouth, etc. (in frontal lobe).
Language shows hemispheric specialization (mostly left hemisphere).
Disorders of Perception
Neglect (Spatial/Hemispatial Neglect)
- Caused by damage to right parietal and temporal lobes.
- Patient ignores one side of space/body (often the left).
- Examples: copying drawings only on one side, ignoring food on one side of a plate.
- Shows how brain lesions affect conscious experience.
- Related to parietal lobe’s role in spatial integration (see parietal damage effects)
Split Brain Studies
- Commissurotomy: cutting the corpus callosum (connection between hemispheres).
- Early patients (1940s–1960s) seemed normal in daily life.
- But experiments revealed:
- Alien hand syndrome (one hand acts independently).
- Split visual fields – what the left visual field sees cannot be verbalized (because right hemisphere has no speech centers).
- These studies demonstrated hemispheric specialization and lateralization of function.
Corpus Callosum
- Connects left and right hemispheres.
- Allows interhemispheric communication.
- Damage/disconnection → classic split-brain phenomena.
