neurodevelopment This occurs for our entire lifetime by the way.
This stage is also where stem cells and progenitor cells become specialized neurons and glia. Explained in Proliferation and Neurogenesis
Dendritic Arborization
Dendrites grow elaborate patterns to receive signals from other neurons. These branches increase in length as time passes (and prunes as needed).

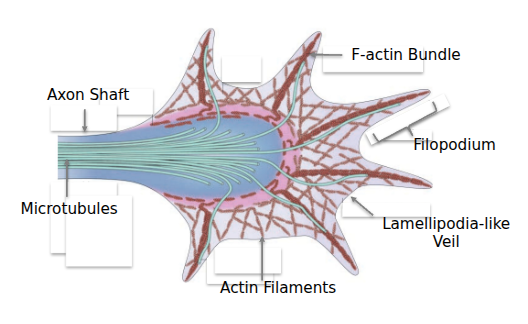
Axonal Growth
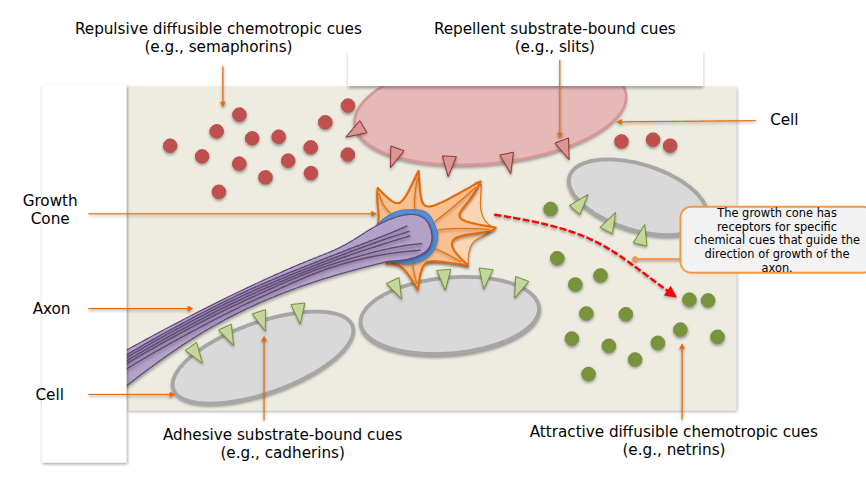
As axons grow, they form Growth Cones. These are special structures at the tip of a growing axon. They have receptors to detect chemical cues that guide them in the right direction of development.
- The repulsive diffusible chemotropic cues and attractive diffusible chemotropic cues can exist to help guide. So are cell receptors.
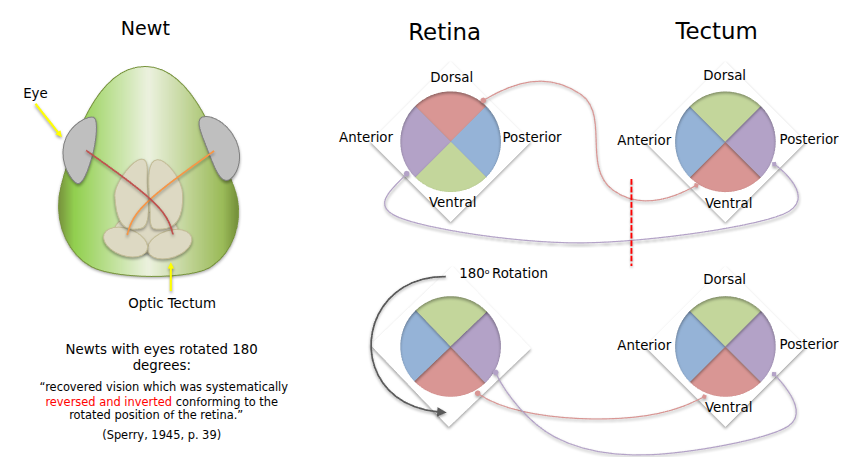
The Newt Experiment
They surgically rotated a newt’s eye 180 degrees. The neurons on the inside were able to reconnect correctly. Shows that there had to have been some sort of physico-chemical intrinsics to guide the neurons back to the right place.
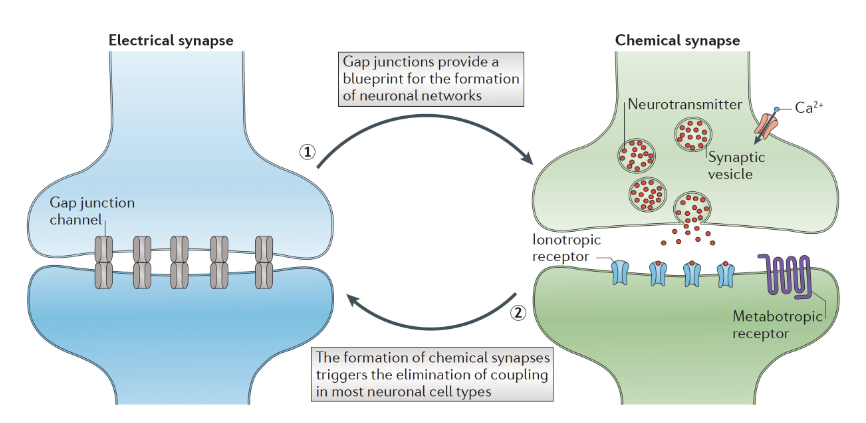
Synaptogenesis
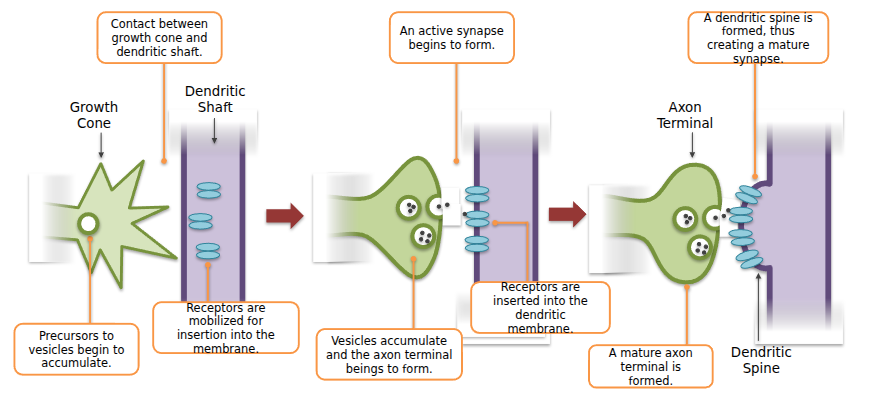
The Dendritic shaft knows what receptors to insert based on signals coming from the axon. The Axon knows what neurotransmitters to release because of its predetermined neuronal identity (result of differentiation, before synaptic formation)
Myelination occurs near the end of Proliferation and Neurogenesis and middles of Migration and Differentiation and Synaptogenesis
After birth our brains begin Synaptic Pruning and Apoptosis
