brain spinalCord peripheralNervousSystem neuroanatomy
Spinal Cord and Peripheral Nervous System
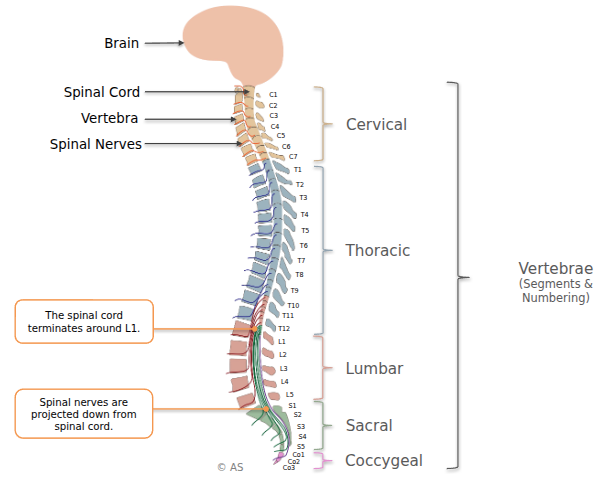
Spinal Cord Anatomy
- CNS = brain + spinal cord.
- Brain includes brainstem, forebrain structures
- PNS = spinal nerves + cranial nerves.
- Spinal cord ends around L1 vertebra.
- Nerves extend downward as the cauda equina.
Spinal Nerve Organization
- Cervical (C1–C8)
- Thoracic (T1–T12)
- Lumbar (L1–L5)
- Sacral (S1–S5)
- Coccygeal (Co1–Co3)
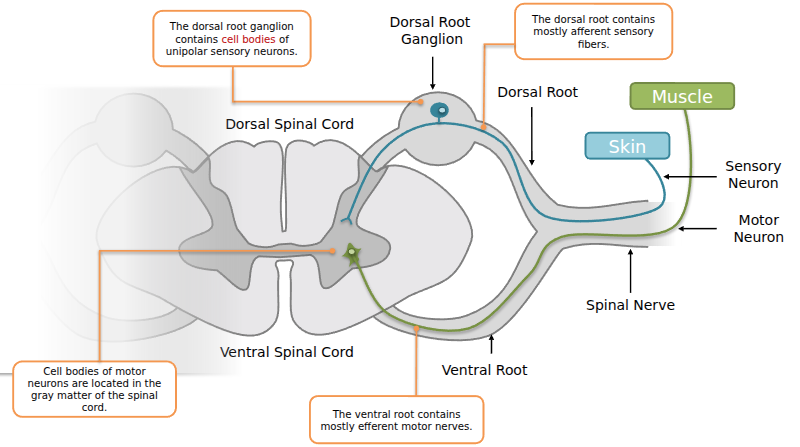
Spinal Cord and Reflexes
- Spinal Nerves branch from the spinal cord. Each has two roots:
- Dorsal root → carries afferent sensory fibers into spinal cord. Cell bodies sit in the dorsal root ganglion.
- Ventral root → carries efferent motor fibers out to muscles. Motor neuron cell bodies are in the spinal cord’s gray matter.
- Together, dorsal + ventral roots form a mixed spinal nerve.
Simple Reflex Arc
- Example: Triceps reflex (deep tendon reflex).
- A stretch receptor in the muscle sends signal via sensory neuron → spinal cord.
- Synapses directly onto a motor neuron → causes contraction.
- Reflexes are fast, involuntary, and involve minimal circuitry.
Cranial Nerves
- 12 pairs, some sensory, some motor, some mixed:
- I. Olfactory – smell
- II. Optic – vision
- III. Oculomotor – eye movement, pupil control
- IV. Trochlear – eye movement
- V. Trigeminal – facial sensation, jaw muscles
- VI. Abducens – eye movement
- VII. Facial – taste, facial expression
- VIII. Auditory (vestibulocochlear) – hearing, balance
- IX. Glossopharyngeal – taste, throat & larynx muscles
- X. Vagus – internal organs
- XI. Accessory – neck muscles
- XII. Hypoglossal – tongue movements
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Divisions
- Somatic Nervous System – voluntary control of skeletal muscles.
- Autonomic Nervous System – involuntary control of organs, glands, smooth muscle.
- Subdivisions:
- Sympathetic (“fight or flight”): pupil dilation, bronchodilation, ↑ HR, ↓ digestion, orgasm, stress hormone release.
- Parasympathetic (“rest and digest”): pupil constriction, salivation, ↓ HR, ↑ digestion, bladder relaxation, sexual arousal.
- Neurotransmitters:
- Sympathetic: preganglionic ACh, postganglionic norepinephrine.
- Parasympathetic: preganglionic ACh, postganglionic ACh.
- Subdivisions:
- Enteric Nervous System – controls digestion independently, but modulated by sympathetic/parasympathetic inputs.
Meninges
- Protective layers surrounding brain and spinal cord:
- Dura mater (outer, tough)
- Arachnoid membrane (middle, web-like) → filled with CSF in subarachnoid space
- Pia mater (inner, thin, hugs brain surface)
- Infections:
- Meningitis = meninges infection → swelling, pressure on brain.
- Encephalitis = infection of brain tissue itself.
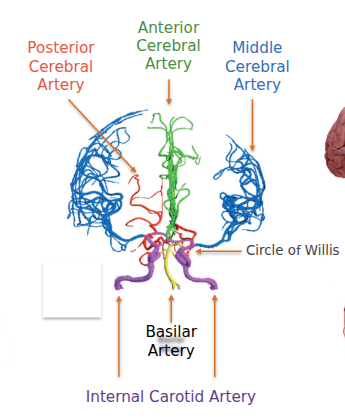
Blood Supply
- Supplied via Circle of Willis: anterior, middle, and posterior cerebral arteries, plus basilar and internal carotid arteries.
- Veins drain into dural venous sinuses → internal jugular vein.
- Critical for preventing ischemia (strokes).
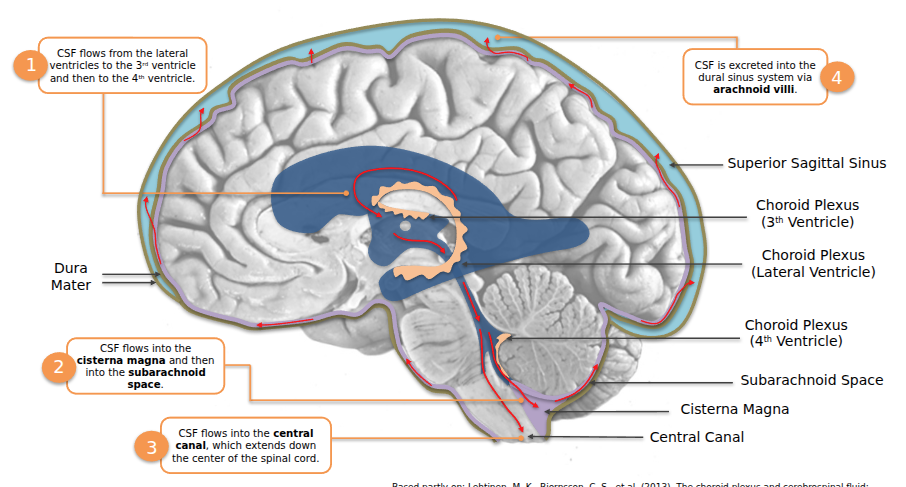
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) and Ventricular System
- Produced by the choroid plexus inside ventricles.
- Pathway: lateral ventricles → 3rd ventricle → cerebral aqueduct → 4th ventricle → central canal & subarachnoid space → absorbed into dural sinuses via arachnoid villi.
- Functions: cushions brain, regulates chemical environment, removes waste, spreads neuromodulators, supports neurogenesis.
- Disorders:
- Hydrocephalus = CSF buildup → enlarged ventricles, compressed brain tissue.
