For review of multivariate calculus, see 00 - Multivariate Calculus Table of Contents.
Normal Distribution (Gaussian) in 1D
Given by
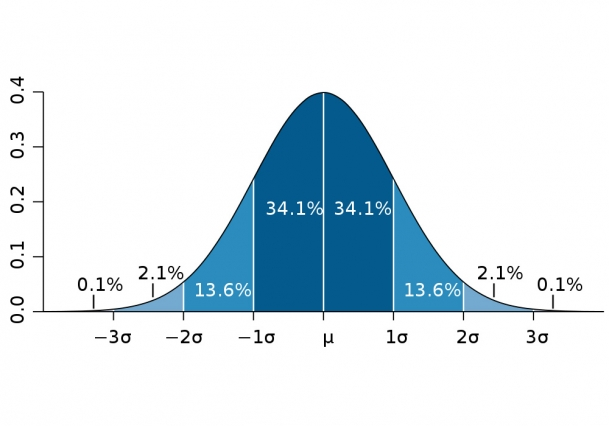
- The higher the the “wider the distribution”
- is the standard deviation, is the variance
Multivariate Gaussian
Given by
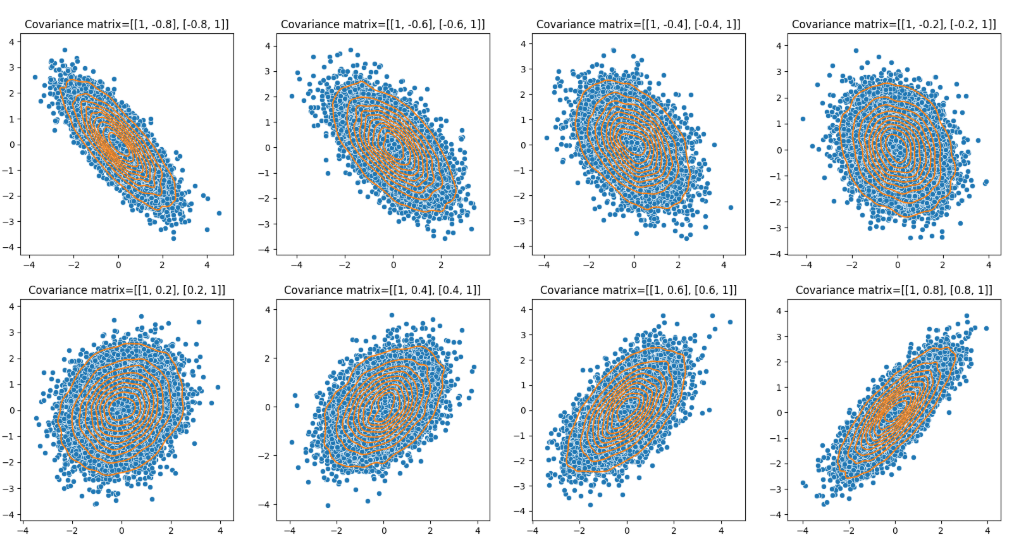 Where is called the covariance matrix, it consists of the following:
Where is called the covariance matrix, it consists of the following:
- Diagonal variance in each dimension
- Off Diagonal covariance between two dimensions
A covariance matrix is, by definition, symmetric.
Linear Change in a Gaussian
We have
It can be shown that if we have a linear transformation
The resultant Gaussian is
Non-Linear Operations on Gaussians
There isn't a nice way of doing something like with with non-linear functions, so we Linearize by approximating a Jacobian near the point of operation
given a non-linear function
where is the measurement noise covariance we linearize like
It can be shown with some work that the resultant
Normalized Product of Gaussians
The normalized product of N gaussians is also a gaussian. Without normalization, we still end up with gaussian shape, just scaled by a constant.
